Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is a disease that is a special form of damage to the spine. Patients with such a disease complain of rapid fatigue, back pain, legs, which causes limiting motor activity. With osteochondrosis, there is a deformation of the intervertebral discs, there is a decrease in their height, dystrophy and Coracoid the growth of vertebrae. When diagnosing on the radiograph, dischanks are clearly visible.
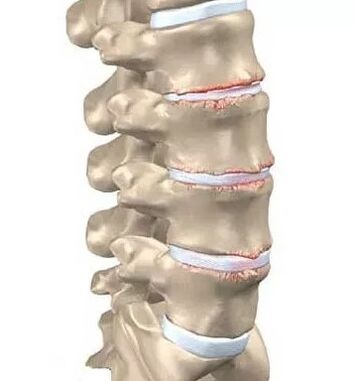
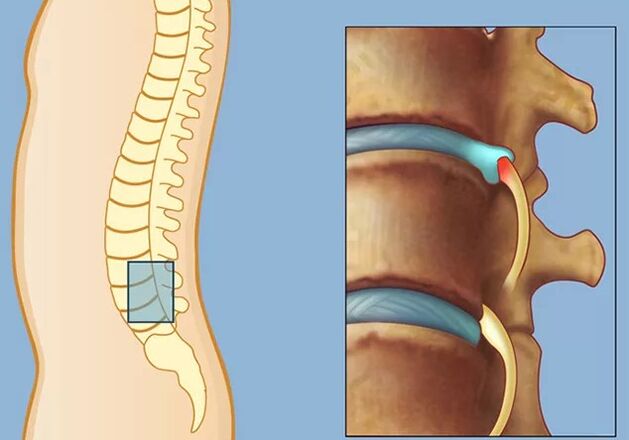
Deformation of cartilaginous tissue during the development of osteochondrosis is a complex process, including biochemical and vascular changes. First of all, the fibrous ring is destroyed, as a result of which Pulpose is introduced into it. As a result, the fibrous ring is torn and the hernia of the disk is formed. In this case, the lower-shine and lower-lover segment is subjected to the highest load. The hernia of the disk, squeezing the spinal cord or its roots, becomes the cause of back pain, which respond in the leg.
The most powerful sciatic nerve in the human body is formed by sacral roots of the spinal cord. It is they, as well as the lower-lover, are irritated with osteochondrosis. From the Latin name of the sciatic nerve, in connection with this, the second name of the disease was formed - Ishias.
Due to the violation of the structure of the cartilage fabric, intervertebral discs, which are special cartilage structures, can no longer fulfill all their functions in full. This leads to the loss of flexibility and mobility of the spine. The processes, which at the initial stages of the disease affect only intervertebral discs, gradually applies to the vertebrae itself.
Discogenic radicolite, which is considered one of the most common symptoms of osteochondrosis, is found in almost every fifth person older than 30 in the world. At risk, people of working age are most often at risk. Osteochondrosis deprives the ability to engage in active activity and often causes disability.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
The main symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis are severe back pain. However, in addition to this sign, there are a number of others. So, patients suffering from this disease are quickly tired, complain about headaches, fatigue and irritability. Discomfort in the back does not allow you to choose a convenient position for sleep, so the body cannot fully relax and recover after the end of the day. The loss of strength forces the patient to minimize physical activity and avoid pain. This leads to the fact that over time he becomes not capable of performing even simple actions, for example, to provide his own household needs.
Problems in the work of the genitourinary system can also be one of the symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis. They appear in the form of pain in the kidney area. In patients with osteochondrosis, urination is disrupted, the unexpected occurrence of causeless discomfort is possible. This leads to the instability of the vertebrae, which due to deformation are not fixed by intervertebral discs. The load on the spine provokes the displacement of the lumbar department from the sacrum when the gravity of the force is exposed to it. Such a process leads to damage to the internal organs, problems in their work. In women, ovaries, appendages and uterus most often suffer, and potency is disturbed in men.
Osteochondrosis is characterized by an increase in the sensitivity of the legs, including stop, hips and lower legs. They are cramps that can lead to full loss of the pulse. The patient’s skin with osteochondrosis on the legs is very dry, peeling and covered with goosebumps in the area of discomfort. During bouts of pain, sweating is disturbed.
All symptoms of osteochondrosis can be classified into the following groups:
Rook syndrome
The thinning of the intervertebral discs leads to the loss of stability vertebrae. Having become mobile, they begin to be annoyed and squeezed blood vessels and nerve roots with sharp movements and heavy physical exertion. This process minimizes pain in the lumbar region, but they resume with renewed vigor where the nerve is compressed. The pain is acute and is drilling. The most very discomfort is expressed in the lower leg, thigh, foot and buttock. Unpleasant sensations make the patient change the gait, leaning into the opposite side of the nerve.
When the nerve roots are irritated for a long time, their inflammation, swelling, venous stagnation and intoxication occur. The pain applies to muscles, ligaments. It is most acute in moments of physical activity, especially if it is carried out without warm -ups immediately after sleep or a state of rest. The pain is often accompanied by increased sweating, which replaces the feeling of chills.
The manifestations of radicular syndrome also include tingling, numbness and loss of sensitivity. The muscles lose their tone, so patients are unable to endure long -term physical activity, for example, go down and lift the stairs, quickly get tired. The functions of the pelvis are disrupted in especially severe cases. In this case, even the occurrence of paralysis and paresis is possible.
Ischemic syndrome
Near nerve roots are blood vessels, which are compressed during deformation. At the first stages of development of osteochondrosis, the arteries are squeezed periodically, but then a spasm acquires a constant character. In this case, a "PUNCTUATE LOME" occurs, the patient must often stop and rest with long walking.
Closing blood vessels leads to the fact that the pelvic organs do not receive the necessary nutrients. This causes pain on the inside of the hips, perineum, in the buttocks up to their paralysis.
Vertebrate syndrome
Under the influence of pain, ischemic and radicular syndrome, the skeleton of the patient with osteochondrosis is deformed. A person begins to stoop, he has a pelvis and spine, the muscles weaken, atrophy. All these changes affect the gait, which is adjusted depending on the area of pain, becomes tense and uncertain. Gradually, the entire musculoskeletal system is exposed to osteochondrosis, and the intervertebral discs continue to collapse.
Pain syndrome (pain with lumbar osteochondrosis)
Unpleasant sensations and discomfort in the back are the main symptoms for osteochondrosis. The nature and strength of pain changes depending on the stage of development of the disease.
At first, it is felt only in the lumbar region at the time of increased voltage of the joints, muscles and ligaments, that is, when performing physical exertion. It may also be constant aching. But with the development of osteochondrosis, acute pain or shift occurs even with sneezing, coughing.
Palpation, as a rule, allows you to determine the seal in the muscles. An attack of pain can last several days, and all this time the patient has to observe bed rest in order to minimize unpleasant sensations in the back. Any sharp movements, weight lifting provoke discomfort.
Causes of lumbar osteochondrosis
The following main reasons for the development of lumbar osteochondrosis are distinguished:
- Uneven load on the spine. According to experts, osteochondrosis is characteristic of a person as a biological species, since it is largely due to his way of life and directness. The need to maintain the position of the body in a certain position requires constant tension of the musculoskeletal system. The optimal load on the spine will be in a standing position. In a lying position on the back, it is minimal, on the side - a little more. But in a sitting position, the load on the lumbar spine increases significantly. The tilt of the body forward creates an additional voltage for the front edge of the vertebrae and spinal column. Therefore, it is recommended to periodically change the position of the body, giving the muscles to relax and shifting the load on the spine, and hold the back straight.
- Hypodynamia. A sedentary lifestyle, the use of a car and public transport, spending a large amount of time for a computer and TV - all this contributes to the development of problems with the spine, including osteochondrosis. A significant part of the population is lacking in motor activity. A passive lifestyle leads to the fact that the musculoskeletal system weakens. In a sitting position, the spine is subjected to maximum load, this becomes the cause of the deformation of cartilage tissue, and as a result, osteochondrosis of the lumbar region. Therefore, it is so important to periodically get up and perform a set of exercises. When a person spends a significant part of the time in a bent position, the bending muscles stretch and lose their tone.
- Too high physical activity. Increased motor activity, like its disadvantage, can also cause osteochondrosis. Back pain is often worried about athletes who are engaged in heavy athletics. This sport requires weight lifting, which creates additional tension for the back muscles and provokes the formation of intervertebral hernias.
- Incorrect posture. In the curved position of the spine, the load on it is distributed unevenly, and this leads to deformation of the intervertebral discs. The same influence is influenced by improper walking. People and elderly people fall at the risk group, since over time, intervertebral discs become less elastic, lose their mobility and are more easily damaged.
- Defects of the bone system and genetic predisposition, injuries and infectious diseases. As a rule, osteochondrosis cause congenital problems with the musculoskeletal system. In addition, the cause of the disease can be the natural fragility of cartilage. Osteochondrosis also develops as a complication after various damage to the spine, osteomyelitis, tuberculosis.
- Flat feet. In patients suffering from flat feet, the set of the foot does not perform depreciation functions, as is the case in normal condition. Thus, when moving, the entire load is taken on the intervertebral discs, as a result of which their rapid wear occurs.
- Overweight. Extra kilograms are a source of additional burden on the heart and the bone muscular system, including the spine. According to statistics, people with overweight are more susceptible to various diseases.
- Inflammatory processes in the body. The development of osteochondrosis is facilitated by factors such as hormonal changes, problems with the joints of the spine, for example, rheumatoid arthritis, impaired endocrine, digestive and cardiovascular system.
- Life. Many patients do not pay due attention to their health: they move little, do not get enough sleep, eat incorrectly. This leads to increased fatigue, violation of the psycho -emotional state, stress. All this makes the body very vulnerable and contributes to the development of lumbar osteochondrosis.
Degree of osteochondrosis of the lumbar
There are 4 degrees of osteochondrosis of the lumbar:
- Cracks appear inside the fibrous ring, which are filled with a substance from the jet nucleus, which causes irritation. At this stage, the deformation of the intervertebral discs is poorly expressed and manifests itself in the form of reflex-boolery symptoms. The patient can complain about pain in the heart, lower back. In the back of the cause of discomfort, sharp movements, weight lifting become. Depending on the character, 2 types of pain are distinguished: lumbalia and lumbago. In the first case, it is stable, and in the second it occurs suddenly;
- The destruction of the fibrous ring continues. However, there is a reduction in the gap between the vertebrae, the nerve endings are pinched. At this stage, a phenomenon as Pseudospondylolisthesis of the lumbar region is characteristic. This is the name of the process of displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other, which leads to pinching of the nerve endings and causes pain. The spine is characterized by unusual mobility. With osteochondrosis of the 2nd degree of degree, patients complain of pronounced discomfort in the back, in the lumbar region, heat and cold are felt alternately. The pain is manifested by seizures, during which goosebumps appear on the skin and intensification intensifies;
- The fibrous ring is finally torn, and the jacket nucleus is squeezed outside. Intertevertebral hernia appears. Squeezing the nucleus into the area of the spinal canal leads to squeezing the vessels and roots of the spinal nerves.
Spine deformation is formed by lordosis, kyphosis or scoliosis. With lordosis, the spine is converted forward. Such a violation of its normal position greatly complicates the work of internal organs and their systems. With kyphosis, the upper spine is curved, and a sensation of stooping in advanced cases occurs. The lateral curvature is manifested in the form of scoliosis. When a patient suffering from osteochondrosis with such a curvature of the spine leans forward, asymmetry becomes noticeable thanks to the protruding blade or rib;
- The last stage of osteochondrosis is the most dangerous, since the spine is finally deformed, which makes full -fledged motor activity impossible. Bone growths become noticeable on the radiograph. Although the pain does not bother the patient for some time, this does not indicate an improvement. 4 degree of osteochondrosis most often ends with disabilities.






































